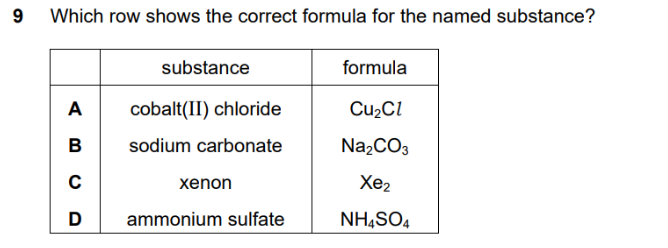
The correct answer is B, sodium carbonate (Na2CO3).
Let’s check each option based on the correct chemical formulas and naming conventions:
- A. Cobalt(II) chloride: The correct formula for cobalt(II) chloride is CoCl2. The Roman numeral (II) indicates that cobalt has a charge of +2 (Co2+). Since chloride ions have a -1 charge (Cl−), two chloride ions are needed to balance the charge.
- B. Sodium carbonate: The sodium ion has a +1 charge (Na+). The carbonate ion has a -2 charge (CO32−). To balance the charges, you need two sodium ions for every one carbonate ion, making the correct formula Na2CO3.
- C. Xenon: Xenon is a noble gas and exists as individual atoms. Its formula is simply Xe, not Xe2. Noble gases are monatomic.
- D. Ammonium sulfate: The ammonium ion has a +1 charge (NH4+). The sulfate ion has a -2 charge (SO42−). To balance the charges, you need two ammonium ions for every one sulfate ion. The correct formula is (NH4)2SO4.
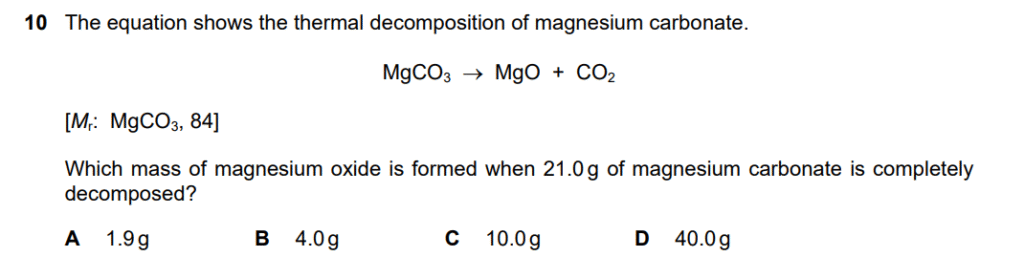
- Calculate the number of moles of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3).
- The formula for calculating moles is: moles= Given Mass / Mr
- Mass of MgCO3 = 21.0g.
- The relative formula mass (Mr) of MgCO3 = 84.
- moles of MgCO3=21.0 g / 84 g/mol = 0.25 mol
- Determine the mole ratio between the reactant and product.
- The balanced chemical equation is: MgCO3→MgO+CO2
- The ratio of MgCO3 to MgO is 1:1.
- This means that for every 1 mole of MgCO3 that decomposes, 1 mole of MgO is formed.
- Therefore, 0.25 moles of MgCO3 will produce 0.25 moles of MgO.
- Calculate the mass of magnesium oxide (MgO) formed.
- First, find the relative formula mass (Mr) of MgO.
- Mr of MgO=24+16=40
- Now, use the moles and Mr to find the mass: mass=moles×Mr
- mass of MgO = 0.25 mol × 40 g/mol = 10.0 g
